[자연어 처리] 파이토치 LSTM 구현
이번에는 실제로 LSTM을 구현해보겠습니다.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
torch.manual_seed(1)`torch.nn` 을 활용하여 LSTM cell 을 생성하는 방법은 다음과 같습니다.
* `input_size` : The number of expected features in the input x
* `hidden_size` : The number of features in the hidden state h
lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size)# input_size: 3, hidden_size: 3 으로 설정하여 LSTM cell 을 생성합니다.
lstm = nn.LSTM(3, 3)LSTM cell 을 생성한 후에는, 입력으로 들어갈 input x, hidden state h, cell state c 를 생성해야 합니다.
위에서 정한 input_size 와 hidden_size 를 고려하여 inputs 와 hidden (h 와 c) 을 생성해 봅시다.
# sequence length 가 5 인 input을 생성합니다.
# 이때, input_size 를 3 으로 설정했으므로, 3 차원 벡터 5개를 생성해야 합니다.
inputs = [torch.randn(1, 3) for _ in range(5)]
# lstm 은 input x 와 hidden state h 를 입력으로 받기 때문에, hidden state 도 생성해 줍니다.
# 이때, hidden_size 를 3 으로 설정했으므로, 3 차원 벡터를 생성합니다.
# lstm 의 입력으로 들어가는 h 는 RNN 에서의 hidden state 와, lstm 에서 등장한 개념인 cell state 로 구성되어 있기 때문에
# hidden 은 3 차원 벡터 2개로 구성되어야 합니다.
hidden = (torch.randn(1, 1, 3),
torch.randn(1, 1, 3))방법 1: Sequence length 가 5 인 input 에 대하여 한 번에 하나의 element 를 lstm cell 에 통과시킵니다.
방법 2: 전체 시퀀스를 한번에 통과시키는 방법도 있습니다.
LSTM 이 반환하는 출력의 첫 번째 값은 전체 시퀀스에 대한 통과한 hidden state 이고, 두 번째 값은 마지막 step 의 hidden state 입니다. out 과 hidden 의 size 를 비교해보세요.
inputs = torch.cat(inputs).view(len(inputs), 1, -1) # 방법 2 를 적용하기 위해 input 을 list 가 아닌 하나의 tensor 로 concat 해줍니다.
hidden = (torch.randn(1, 1, 3), torch.randn(1, 1, 3)) # 방법 2 를 적용하기 위해 hidden 을 다시 초기화합니다.
out, hidden = lstm(inputs, hidden)
print(out)
print(hidden)LSTM 을 이용해 Part-of-Speech (PoS) Tagging 을 하기 위해 학습 데이터를 준비합니다.
- training_data 에는 단어 시퀀스와 각 단어의 품사 태그를 준비해야 합니다.
- word_to_ix: 모델의 입력으로 사용하기 위해 각 단어를 id 로 mapping 합니다.
- tag_to_ix: 품사 태그 또한 id 로 mapping 합니다.
def prepare_sequence(seq, to_ix):
idxs = [to_ix[w] for w in seq]
return torch.tensor(idxs, dtype=torch.long)
training_data = [
# Tags are: DET - determiner; NN - noun; V - verb
# For example, the word "The" is a determiner
("The dog ate the apple".split(), ["DET", "NN", "V", "DET", "NN"]),
("Everybody read that book".split(), ["NN", "V", "DET", "NN"])
]
word_to_ix = {}
# For each words-list (sentence) and tags-list in each tuple of training_data
for sent, tags in training_data:
for word in sent:
if word not in word_to_ix: # word has not been assigned an index yet
word_to_ix[word] = len(word_to_ix) # Assign each word with a unique index
print(word_to_ix)
tag_to_ix = {"DET": 0, "NN": 1, "V": 2} # Assign each tag with a unique index
# These will usually be more like 32 or 64 dimensional.
# We will keep them small, so we can see how the weights change as we train.
EMBEDDING_DIM = 6
HIDDEN_DIM = 6{'The': 0, 'dog': 1, 'ate': 2, 'the': 3, 'apple': 4, 'Everybody': 5, 'read': 6, 'that': 7, 'book': 8}
Embedding layer, output layer, lstm cell 을 포함한 LSTMTagger 모듈을 정의합니다.
- embeds: input id 를 embedding layer 로 encode 하여 input 에 해당하는 embedding 생성합니다.
- lstm_out: embedding 을 lstm 에 통과하여 전체 시퀀스에 대한 hidden state 를 저장합니다.
- tag_space: lstm 의 output 인 hidden 을 이용해 존재하는 tag (DET, NN, V) 공간으로 linear transform 합니다.
- tag_scores: 이후 softmax 를 적용하여 각 tag 가 될 score 를 측정합니다.
class LSTMTagger(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embedding_dim, hidden_dim, vocab_size, tagset_size):
super(LSTMTagger, self).__init__()
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
# The LSTM takes word embeddings as inputs, and outputs hidden states
# with dimensionality hidden_dim.
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim)
# The linear layer that maps from hidden state space to tag space
self.hidden2tag = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, tagset_size)
def forward(self, sentence):
embeds = self.word_embeddings(sentence)
lstm_out, _ = self.lstm(embeds.view(len(sentence), 1, -1))
tag_space = self.hidden2tag(lstm_out.view(len(sentence), -1))
tag_scores = F.log_softmax(tag_space, dim=1)
return tag_scoresmodel 을 build 하고, 학습에 필요한 loss 함수와 optimizer 를 선언합니다.
model = LSTMTagger(EMBEDDING_DIM, HIDDEN_DIM, len(word_to_ix), len(tag_to_ix))
loss_function = nn.NLLLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)이제, training data 를 이용해 모델을 학습합니다. 즉, input 을 LSTMTagger 에 통과시켜 각 단어의 PoS tag 를 예측하고, 정답 tag 와 비교하여 loss 를 계산한 후 loss 를 backpropagate 하여 모델 파라미터를 업데이트 합니다
for epoch in range(300): # again, normally you would NOT do 300 epochs, it is toy data
for sentence, tags in training_data:
# Step 1. Remember that Pytorch accumulates gradients.
# We need to clear them out before each instance
model.zero_grad()
# Step 2. Get our inputs ready for the network, that is, turn them into
# Tensors of word indices.
sentence_in = prepare_sequence(sentence, word_to_ix)
targets = prepare_sequence(tags, tag_to_ix)
# Step 3. Run our forward pass.
tag_scores = model(sentence_in)
# Step 4. Compute the loss, gradients, and update the parameters by
# calling optimizer.step()
loss = loss_function(tag_scores, targets)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
LSTM 이 아닌 GRU 를 사용하려면 nn.GRU 를 활용할 수 있습니다.
위처럼 학습 데이터만 활용해 모델을 평가할 경우 모델의 generalization 성능이 어떻게 되는지 평가하기 어렵습니다. 학습시 보지 못한 새로운 데이터를 이용해 모델을 평가해야 합니다. 주어진 데이터를 train, test 로 split 하거나 cross-validation 방법을 활용해야 합니다.
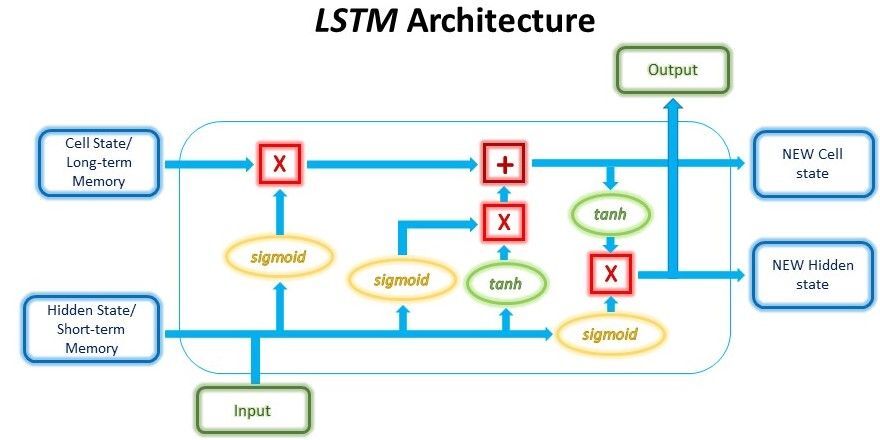
Reference: https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/nlp/sequence_models_tutorial.html